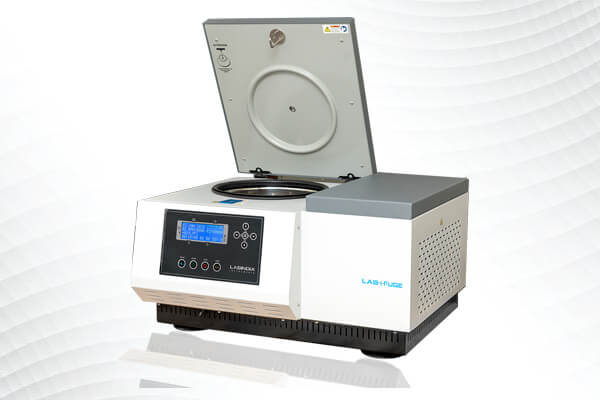
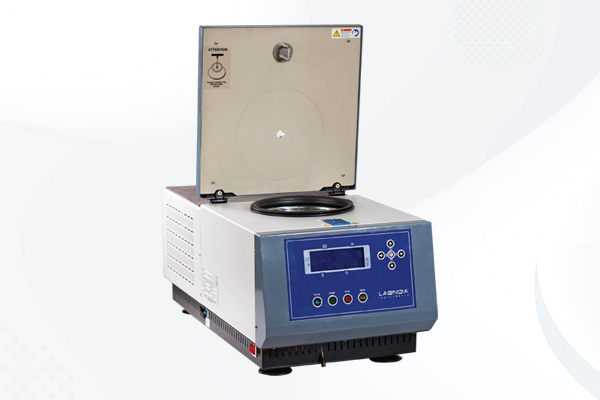
Labindia announces the launch of the Centrifuge - "Lab-i-Fuge"
Centrifuge works by separating two materials based on different densities. They are best used to separate materials that have similar densities or when insoluble particulates are present in a dissolved solution
It is one of the necessary lab instruments which is widely used in all kinds of laboratories like research institutes, pharmaceuticals, hospital, and university.
Some common applications for centrifuges are listed below:
- Separation of mixtures with close densities
- Separate immiscible liquids
- Sediment suspended solids
- Separation of blood components
- Separation insoluble particles (e.g. insoluble proteins in a protein solution)
- Isotope Separation
- Gravity simulation environments for astronauts
- Separating creams
- Spin Column function
- Separation of wastewater sludge
- Material synthesis in a high gravity environment etc.
There are many types of centrifuge available in the market today, of which the two main factors are rotor speed and centrifuge size.
Labindia is a laboratory centrifuge manufacturer and supplier in India. The product description will help you to get the overview of the LAB-i-FUGE and the features of the product which makes best in their segment. Labindia LAB-i-FUGE (Refrigerated/Non Refrigerated) is bench top centrifuge with a high speed.
Before performing any activity, users can set up the separation process in the LAB-i-FUGE system in advance as per their requirement. This has been designed with the features of pre-set data in which you can set 99 different programs so when you are ready for the work, you are just a few clicks away, because you have already pre-set the program in the instrument.
To perform the activity on the LAB-i-FUGE machine, provide different types of rotors which can be set up at a variable speed and can go to a max of 20,000 RPM.for eg Fixed angle rotor, swing angle rotor. In a fixed angle rotor the rotor spins at 45- degree angle, in a Swing angle the rotor spins at a 90-degree angle.
Its ergonomic design helps working efficiently which ensures operator safety. While using the centrifuge machine, it is necessary to balance the rotor while spinning at a high speed. Placing the tube in the opposite directions keeps the centrifuge rotor gravity in the centre.
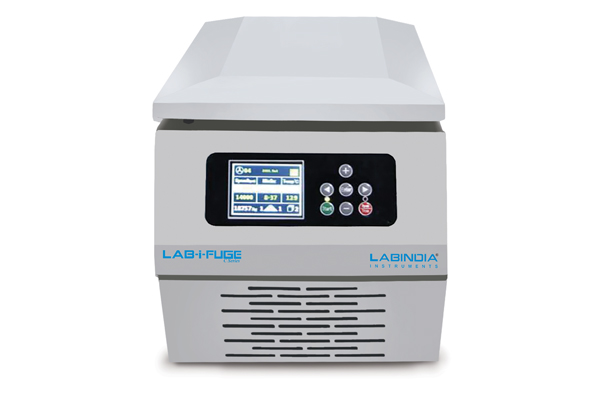

Table Top High Speed Refrigerated Centrifuge
LAB-i-FUGE C Series high speed refrigerated centrifuge is widely used in clinical medicine, biochemistry, genetic engineering, immunology, etc. It is an indispensable instrument for centrifugation at all levels of hospitals, research institutes, and universities.
Read More Request Quote
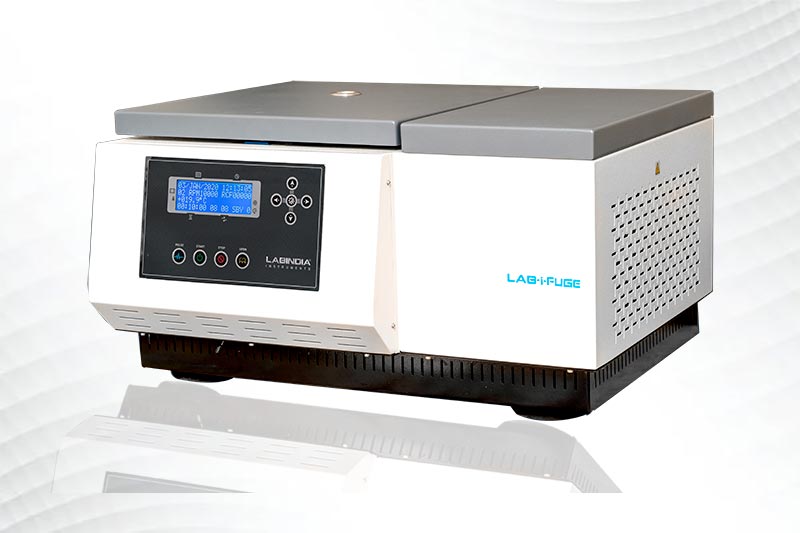

The Labindia Lab-i-fuge system delivers outstanding performance and reliability in the laboratory for centrifugation application. This innovative centrifuge offers exceptional quality for consistent result, unmatched productivity, versatility, performance and easy usage.
Read More Request Quote
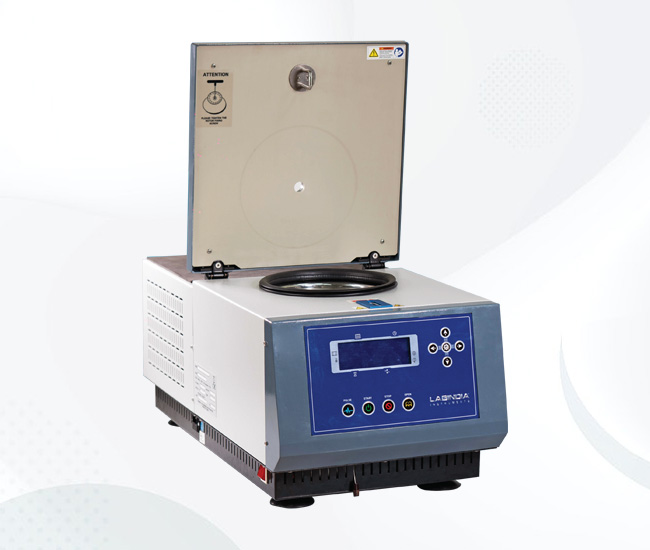

Lab i Spin is a Refrigerated bench top Centrifuge .It is Ideal for Hospitals , blood bank and covid testing Labs
Read More Request Quote
Are you looking for Centrifuge Suppliers who can offer a Centrifuge for your
applications but unsure which one will best meet your needs?
If so, look no further than Labindia Instruments, among the leading centrifuge
manufacturers in Mumbai, known for a wide collection of world-class
centrifuge machines.
As one of the top Centrifuge Machine Manufacturers, Labindia Instruments
offers benchtop centrifuges. Laboratory centrifuge, with the best design for any
kind of laboratory experiment.
RPM / RCF - Concept
It indicates as to how quickly the centrifuge will spin and how much resultant force
will be applied. When talking about force, relative centrifugal force is considered
more important as it functions as the resultant force that is exerted on the
substances in the vessels.
Centrifuges in Labindia Instruments’ collection of centrifuge machines have an
RPM of up to 20,000 and an RCF of 32’198* g
CENTRIFUGE ROTORS
A centrifuge machine comes with some accessories and rotors. The rotors come with their own unique characteristics which are detailed here as
follows:
- VESSEL COMPATBILITY: Every Centrifuge Machine comes in appropriate sizes. Additionally, they come with rotor options that are compatible with the vessel of choice.
- ROTOR’S STYLE: Centrifuge machines come with different styles. They are mostly fixed angle and rotors with options like Swing Out rotors, Vertical Rotors, PCE rotors; & Microlite Rotors. Additionally, the centrifuges have alternatives for one or other centrifuge counterparts; and on occasions, both.
- TEMPERATURE RANGE: Different types of centrifuges operate at room temperature sans cooling or heating options of any kind. When it comes to cooling types, they usually drop down to temperatures that are either - 9° C or - 40° C.
- MAXIMUM RCF: The maximum RCF of the centrifuge should be factored in and also noted only if is achievable.
Generally, handling of centrifuges carries with it several safety risks. However, the Centrifuge Machines from Labindia Instruments come well-equipped with quality safety features that will guarantee protection to users as well as the surrounding environment.
- ELECTRIC LID LOCK: It prevents the accidental opening of the centrifuge lid, when the centrifuge is in working mode.
- IMBALANCE SENSOR: It detects any imbalance in the centrifuge and simultaneously puts the centrifuge on hold if the vibration level is increased.
- SEALED ROTORS: They prevent the occurrence of leakages or spillages of biohazard chemicals or substances during the work-process.
- ROTOR RECOGNITION TECHNOLOGY: It detects which rotor type is installed. Additionally, it makes sure that the rotor does not gain speeds that are greater than the maximum operating speed.
A Centrifuge Machine works in accordance with the principle of sedimentation.
The principle of sedimentation operates under the influence of centrifugal force and gravitational force. This will facilitate the separation of the substances in line with their densities.
A powerful motor at the center of the centrifuge machine creates spin. Then there is the rotor attached to the motor in which the containers that hold the tubes containing the material to be centrifuged, rest. The containers can be spun at either at a 45-degree angle (called fixed angle centrifuge); or a 90-degree angle (called horizontal centrifuge); or no angle at all (called vertical centrifuge). The tubes may either be loaded, depending on the type of centrifuge, at the angle on which they will rotate; or get loaded into a container that adjusts itself to a different angle when started.
CENTRIFUGE MACHINE USES
There are many types of centrifuges available in the market. This has enabled them to be used for a variety of applications.
Like separation of immiscible liquids; separation of blood; separation of insoluble particles like insoluble proteins in a protein solution; separation of mixtures with close densities; isotope separation; separation of creams; separation of wastewater
sludge; material synthesis in a high gravity environment; gravity simulation environment for astronauts; and not to forget, washing machine spin function.
Aside from the above, they are also used for
- Separation of blood products (performed by a laboratory centrifuge).
- Separation of materials that have identical identities.
- Separation of a mixture containing two dissimilar miscible liquids.
- Fractionating of numerous sub-cellular organelles; and also the analysis of membranes.
FAQs
Centrifugation is the technique of separating components where the centrifugal force/ acceleration causes the denser molecules to move towards the periphery while the less dense particles move to the centre.
Centrifugation is a technique used for the separation of particles from a solution according to their size, shape, density, viscosity of the medium and rotor speed.
- The process of centrifugation relies on the perpendicular force created when a sample is rotated about a fixed point.
- The rate of centrifugation is dependent on the size and density of the particles present in the solution.
Centrifugation uses a centrifuge, or a device that can rapidly spin, to speed up this process. Imagine we put the mixture into test tubes, and those tubes into the centrifuge. The centrifuge holds the top of the tubes, and the bottom is allowed to angle out. As it spins, the larger particles would get flung out farther, and smaller particles would stay close to the centre.
Centrifugation techniques take a central position in modern biochemical, cellular and molecular biological studies. Depending on the particular application, centrifuges differ in their overall design and size.
Many different types of centrifuges are commercially available including :
- large-capacity low-speed preparative centrifuges
- preparative high-speed ultracentrifuges
- refrigerated preparative centrifuges/ultracentrifuges
- analytical ultracentrifuges
- large-scale clinical centrifuges
- small-scale laboratory microfuges.
Relative centrifugal force is the measure of the strength of rotors of different types and sizes. This is the force exerted on the contents of the rotor as a result of the rotation.
RCF is the perpendicular force acting on the sample that is always relative to the gravity of the earth. The RCF of the different centrifuge can be used for the comparison of rotors, allowing the selection of the best centrifuge for a particular function. The formula to calculate the relative centrifugal force (RCF) can be written as:
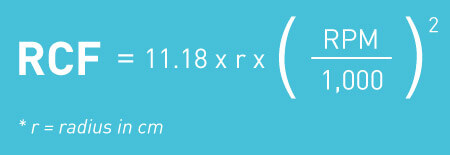
RCF (g Force) = 1.118 × 10-5 × r × (RPM) 2
Where r is the radius of the rotor (in centimetres), and RPM is the speed of the rotor in rotation per minute.
Revolutions per Minute (RPM) in regards to centrifugation is simply a measurement of how fast the centrifuge rotor does a full rotation in one minute. Centrifuges will have a speed range that they are capable of achieving and will vary depending on the centrifuge. A low speed centrifuge might spin at as low as 300 RPM, whilst a high speed centrifuge could spin up to 15000 RPM or even more. Ultracentrifuges are also available and are the most powerful type of centrifuge, they can spin in excess of 150,000 RPM.
Centrifuges are used in various laboratories to separate fluids, gases, or liquids based on density. In research and clinical laboratories, centrifuges are often used for cell, organelle, virus, protein, and nucleic acid purification.
There are two very common rotor designs :
- Fixed angle
- Swinging bucket
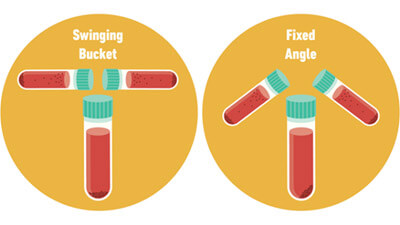
The fixed angle rotor is designed to hold tubes in a fixed position at a fixed angle relative to the vertical axis of rotation (up to about 45°). Centrifugation will cause particles to sediment along the side and bottom of the tube. Fixed angle rotors are ideal for pelleting applications either to remove particles from a suspension and discard the debris or to recover the pellet.
The swinging bucket design allows the tubes to swing out from a vertical resting position to become parallel to the horizontal during centrifugation. As a result, sediment will form along the bottom of the tube, swinging bucket rotors are best for separating large volume samples at low speeds and resolving samples in rate-zonal (density) gradients.
If you follow a given protocol, make sure to use the same type of rotor and apply the given relative centrifugal force (rcf or g × force) as well as the same temperature and running time. In general, the following major parameters have to be determined to achieve a successful centrifugation run:
- Type of sample
- Type of vessel
- Type of centrifuge
- Type of rotor
- Necessary relative centrifugal force
- Necessary temperature during centrifugation
It is essential to select a centrifuge that is suited to the specific application. When purchasing a centrifuge, it is important to consider the following questions:
- What sample volumes are you working with? For processes involving large or varying volumes, a floor-standing model with higher capacity and different rotor configurations may be the best solution.
- Are samples temperature sensitive? If so, a centrifuge with refrigeration and temperature control options is required.
- Will the centrifuge be used for processing clinical or blood banking samples? Cell washers or clinical models are available for these specific applications.
- How much laboratory space is available vs the centrifuge footprint?
- What is the maximum g-force the centrifuge is capable of generating? Low-speed centrifuges are ideal for separating whole cells, while ultracentrifuges are necessary for separating DNA and RNA.
To separate cellular and subcellular components, separating one cell type from another.
Removing cells or other suspended particles from their surrounding milieu on either a batch or a continuous-flow basis.
Isolating viruses and macromolecules, including DNA, RNA, proteins, and lipids or establishing physical parameters of these particles from their observed behaviour during centrifugation.
To study the effects of centrifugal forces on cells, developing embryos, and protozoa.


